Understanding Sedation in Pediatric Dentistry: Choices, Benefits, and Risks
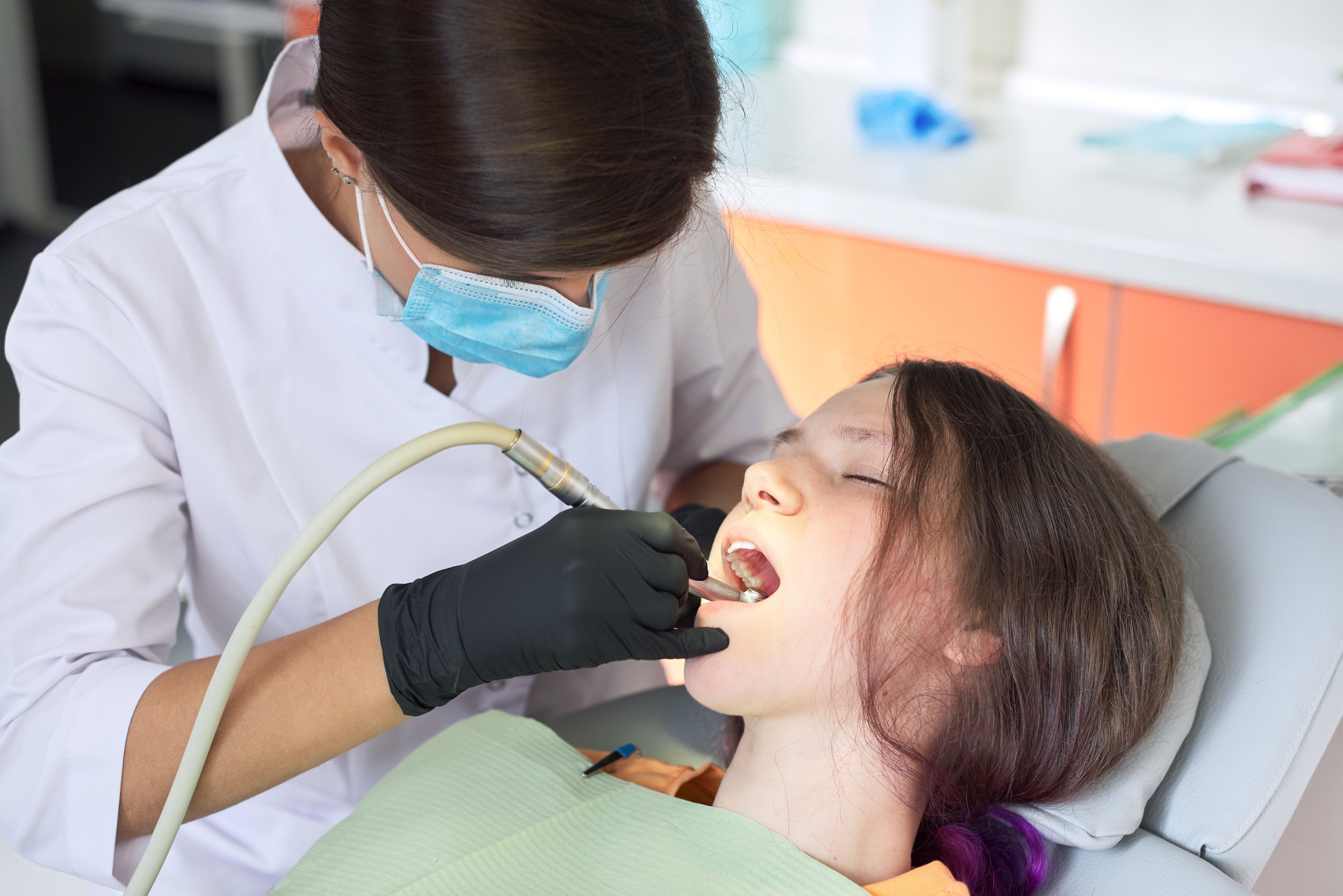
Ensuring the comfort and safety of our young dental patients during dental procedures is paramount. Treating pediatric dental patients, one of the ways we achieve this is through sedation. There are different types of sedation used in pediatric dentistry, each with its own benefits, risks, and appropriate use cases. Today, we'll explore two common methods: oral conscious sedation and general anesthesia.
Oral Conscious Sedation
What is it? Oral conscious sedation involves administering medication orally to help a child relax during dental procedures. The child remains awake but is in a state of calm and can follow instructions.
Benefits:
Reduced Anxiety: It helps children who are anxious or fearful to feel more relaxed and comfortable.
Pain Control: Provides effective pain management during procedures.
Memory: Often results in little to no memory of the procedure, reducing future anxiety.
Risks:
Side Effects: Potential for nausea, vomiting, and allergic reactions are most common but not all.
Respiratory Issues: In rare cases, it can cause respiratory depression.
Effectiveness: The level of sedation can vary based on the child's metabolism and response to the medication.
When to Use: Oral conscious sedation is generally considered for children who are moderately anxious or need to undergo longer or more complex procedures. It is typically used for children over the age of three, as younger children may not respond predictably to the medication.
General Anesthesia
What is it? General anesthesia involves administering medication to render the child completely unconscious during the dental procedure. It is usually administered by an anesthesiologist in a hospital or surgical center setting.
Benefits:
Complete Control: The child is entirely asleep, allowing the dentist to perform the procedure without movement or resistance.
Comprehensive Treatment: Multiple procedures can be completed in one session, reducing the need for multiple visits.
Pain-Free: The child will not experience any pain during the procedure.
Risks:
Anesthesia Complications: Includes risks such as allergic reactions, respiratory issues, and, in rare cases, more serious complications.
Recovery Time: Longer recovery period compared to other forms of sedation, with potential for grogginess and disorientation.
Cost: Generally more expensive due to the need for an anesthesiologist and specialized setting.
When to Use: General anesthesia is typically considered for very young children, those with severe anxiety or special needs, or when extensive dental work is required. It is often recommended for children under the age of three who cannot cooperate with the dentist or for whom other forms of sedation are not effective.
Deciding on Sedation
The decision to use sedation, and the type of sedation, depends on several factors:
Age and Development: Younger children may require more profound sedation like general anesthesia, whereas older children may do well with oral conscious sedation.
Anxiety Levels: Children with higher levels of anxiety may benefit from deeper sedation.
Medical History: A thorough medical history is essential to determine the safest sedation method.
Procedure Complexity: More complex or lengthy procedures might necessitate deeper sedation to ensure the child’s comfort and cooperation.
Why Use Sedation?
Sedation in pediatric dentistry is used to:
Manage Anxiety: Helping children who are afraid of the dentist to have a positive experience.
Ensure Cooperation: Making it possible to perform necessary dental work safely and efficiently.
Provide Comfort: Ensuring the child is comfortable and pain-free during procedures.
Prevent Trauma: Reducing the risk of traumatic experiences that can lead to dental phobias later in life.
In conclusion, the use of sedation in pediatric dentistry is a valuable tool for managing anxiety, ensuring comfort, and allowing for the safe completion of dental procedures. Oral conscious sedation and general anesthesia each have their benefits and risks, and the choice between them depends on the child's specific needs and the complexity of the procedure. As always, the safety and well-being of the child are our top priorities, and careful consideration is given to selecting the most appropriate sedation method.
Kids Dental Spot is a dental office focused providing services to pediatric patients in Anaheim, California serving kids, children, infants and adolescents in the heart of Orange County serving nearby neighborhoods, such as: Fullerton, Brea, Garden Grove, Santa Ana, Buena Park, Placentia, and Orange.
Written and Medically Reviewed by Dr. Atiya Bahmanyar, DDS (Board Certified - Doctorate of Dental Surgery)